ΕΡΕΥΝΗΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΩΤΟΚΟΛΛΟ

ΜΕΛΕΤΗ ΤΗΣ ΕΠΙΔΡΑΣΗΣ ΕΛΑΙΟΛΑΔΩΝ ΔΙΑΦΟΡΕΤΙΚΗΣ ΠΕΡΙΕΚΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΣΕ ΦΑΙΝΟΛΕΣ ΣΤΟ ΛΙΠΙΔΑΙΜΙΚΟ ΠΡΟΦΙΛ ΚΑΙ ΤΗΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΤΑΣΗ ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗΣ ΤΟΥ ΑΓΓΕΙΑΚΟΥ ΕΝΔΟΘΗΛΙΟΥ ΣΕ ΑΣΘΕΝΕΙΣ ΜΕ ΥΠΕΡΛΙΠΙΔΑΙΜΙΑ
ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ, ΓΕΝΙΚΟ ΝΟΣΟΚΟΜΕΙΟ ΜΕΣΣΗΝΙΑΣ, ΚΑΛΑΜΑΤΑ
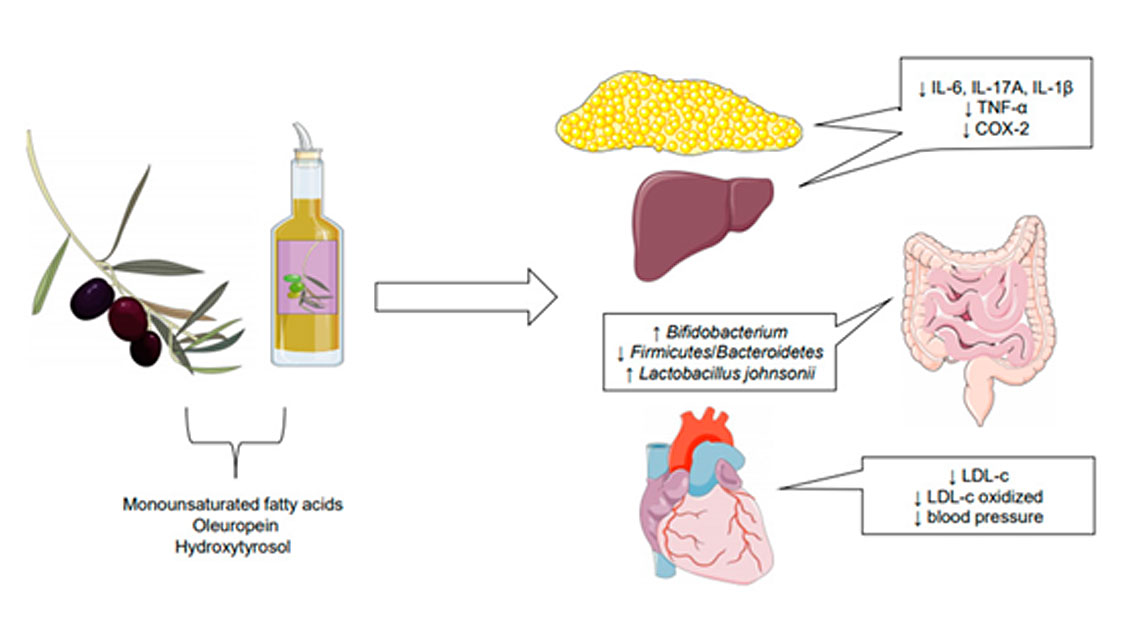
Το ελαιόλαδο (Oleaeuropaea) θεωρείται εξαιρετική πηγή λιπιδίων και σχετίζεται με την πρωτογενή και δευτερογενή πρόληψη της καρδιαγγειακής νόσου, τη βελτίωση του λιπιδαιμικού προφίλ και της ευαισθησίας στην ινσουλίνη, την αυξημένη οξειδωτική σταθερότητα, τη βελτίωση των δεικτών φλεγμονής και τον έλεγχο της αρτηριακής πίεσης (Σχήμα 1). [1,2] Το Σχήμα 1 δείχνει τις επιδράσεις των μονοακόρεστων λιπαρών οξέων, της υδροξυτυροσόλης και της ελευρωπαϊνης στις καρδιαγγειακές παθήσεις, τη φλεγμονή και τη σύνθεση του μικροβιώματος του εντέρου. Το ελαιόλαδο ανήκει στη μεσογειακή διατροφή (MedDiet) η οποία είναι ένα πρότυπο ποιοτικής δίαιτας που παρέχει προστατευτικές επιδράσεις έναντι καρδιαγγειακών παθήσεων, φλεγμονής και καρκίνου. [3]
Η υδροξυτυροσόλη (HT) αντιπροσωπεύει ένα από τα κύρια συστατικά πολυφαινόλης του εξαιρετικά παρθένου ελαιολάδου (Extra Virgin Olive Oil, EVOO) και έχει αντιφλεγμονώδη και αντιτερατογόνο δράση, βελτιώνοντας το λιπιδαιμικό προφίλ, μειώνοντας το οξειδωτικό στρες και ενεργοποιώντας τα κύτταρα φλεγμονής. [4] Επιπλέον, η ελευρωπαϊνη, ένα άλλο αντιοξειδωτικό που βρίσκεται στην πάστα και σε φύλλα ελιάς, σχετίζεται επίσης με βελτίωση φλεγμονωδών παραγόντων σε διάφορα μοντέλα φλεγμονής και προσφέρει αντιπολλαπλασιαστικές και αντικαρκινικές ιδιότητες που επάγουν τη διαδικασία της απόπτωσης των καρκινικών κυττάρων, κυρίως στο παχύ έντερο. [1,5,6] Σύμφωνα με τον κανονισμό της Επιτροπής (ΕΕ) αριθ. 432/2012, για να θεωρούνται οι πολυφαινόλες προστατευτικές έναντι οξειδωτικών επεισοδίων, το ελαιόλαδο πρέπει να περιέχει τουλάχιστον 5 mg HT ανά 20 g ελαιολάδου. [7] Το EVOO λαμβάνεται με τη διαδικασία της μηχανικής συμπίεσης της ελιάς χωρίς να υποβληθεί σε οποιοδήποτε άλλο είδος παρέμβασης, εκτός από τα στάδια πλύσης, φυγοκέντρησης και διήθησης. Αυτές οι διαδικασίες επιτρέπουν τη διατήρηση συστατικών, τα οποία αποτρέπουν οξείδωση του λαδιού. [6]
Η κατανάλωση πολυφαινολικώνελαιολάδων στα πλαίσια της Μεσογειακής διατροφής, έχει δειχθεί ότι βοηθάει στην πρωτογενή πρόληψη μειώνοντας τις παραμέτρους κινδύνου εμφάνισης καρδιαγγειακών συμβαμάτων, όπως φλεγμονωδών κυταρροκινών (ιντερλευκίνη-6), αυξάνει τα επίπεδα της λιποπρωτεΐνης υψηλής πυκνότητας (HDL-c) και μειώνει τα επίπεδα της λιποπρωτεΐνης χαμηλής πυκνότητας LDL-c. [2] Η ενδοθηλιακή δυσλειτουργία έχει ως αποτέλεσμα τη συσσώρευση μορίων προσκόλλησης που προκαλούν αγγειακές βλάβες. Τα μόρια προσκόλλησης συντίθενται σε ενδοθηλιακά κύτταρα και η παραγωγή τους διεγείρεται από φλεγμονώδεις κυταρροκίνες, όπως η ιντερλευκίνη 1 (IL-1) και ο παράγοντας νέκρωσης όγκου a (TNF-a). Σε υγιή άτομα, συμβαίνει καταστολή τέτοιων μορίων προσκόλλησης που έχει ως αποτέλεσμα τη μείωση των καρδιαγγειακών συμβαμάτων [8].
Η κατανάλωση EVOO μπορεί επίσης να δράσει ευεργετικά στη δευτερογενή πρόληψη ασθενών, δεδομένου ότι περιορίζει την LDL-c και αυξάνει τη συγκέντρωση της HDL-c, γεγονός που διευκολύνει την αντίστροφη μεταφορά χοληστερόλης και μειώνει τον κίνδυνο μελλοντικών καρδιαγγειακών συμβαμάτων [1,9,10].
Ωστόσο τα δεδομένα σχετικά με τη δράση των πολυφαινολικώνελαιολάδων παραμένουν ακόμα περιορισμένα. Θέλουμε να αποδείξουμε ότι η κατανάλωση πολυφαινολικού ελαιολάδου από το Νομό Μεσσηνίας έχει ευεργετική επίδραση στην υγεία ασθενών και υγιών. Πρωτεύων σκοπός της μελέτης μας είναι να εξετάσουμε την ευεργετική επίδραση του πολυφαινολικού ελαιολάδου ELETTRA από την οικογένεια ΜΠΟΥΖΑΛΑ στην Κλεισούρα Μεσσνίας στην επίδραση του λιπιδαιμικού προφίλ και σε επίπεδο φλεγμονής και λειτουργίας του αγγειακού ενδοθηλίου σε υπερλιπιδαιμικούς ασθενείς και σε υγιή άτομα. Δευτερεύων σκοπός είναι να διερευνήσουμε την ύπαρξη διαφορών ανάμεσα σε ελαιόλαδα διαφορετικής περιεκτικότητας σε φαινόλες.
ΔΕΙΤΕ ΟΛΟ ΤΟ ΕΡΕΥΝΗΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΩΤΟΚΟΛΛΟ
