ΤΟ ΑΓΛΥΚΟ ΤΟΥ ΛΙΓΚΣΤΡΟΣΙΔΗ ΕΜΦΑΝΙΖΕΙ ΠΟΛΛΑΠΛΑΣΙΑΣΤΙΚΗ ΔΡΑΣΗ ΕΝΑΝΤΙ ΤΟΥ ΚΑΡΚΙΝΟΥ ΤΟΥ ΗΠΑΤΟΣ
Αντιπολλαπλασιαστικές δράσεις εκχυλισμάτων ελαιολάδου πλούσια σε ελαιοκανθάλη και άγλυκου του λιγκστροσίδη σε ανθρώπινες κυτταρικές σειρές καρκίνου του ήπατος.
Σε αυτή την ερευνητική εργασία, η De Stefanis και η ερευνητική της ομάδα, διερεύνησαν την αντικαρκινική δράση του άγλυκου του λιγκστροσίδη στο ηπατοκυτταρικό καρκίνωμα. Το ηπατοκυτταρικό καρκίνωμα είναι ένας κακοήθης όγκος με υψηλά ποσοστά θνησιμότητας. Η συστηματική χημειοθεραπεία είναι οριακά μόνο αποτελεσματική και συχνά έχει ως επακόλουθο μεγάλη τοξικότητα. Οι κυτταρικές σειρές ηπατοκυτταρικού καρκινώματος γίνονται πιο ευαίσθητες στην ταξόλη όταν η θεραπεία συνδυάζεται με τον Παράγοντα Νέκρωσης Όγκων α (TNFα). Η παρούσα εργασία στόχευσε στην αξιολόγηση της επιδράσης ενός πολυφαινολικού εκχυλίσματος που περιέχει τόσο ελαιοκανθάλη όσο και άγλυκου του λιγκστροσίδη στον πολλαπλασιασμό και/ή στο κυτταρικό θάνατο σε τρεις κυτταρικές σειρές καρκίνου του ήπατος (HepG2, Huh7 και Hep3B).
Διερευνήθηκε επίσης η πιθανότητα ενίσχυσης αυτού του αποτελέσματος με την προσθήκη TNFa. Τόσο ο κυτταρικός πολλαπλασιασμός όσο και ο κυτταρικός θάνατος ενισχύθηκαν από την έκθεση στο πολυφαινολικό εκχύλισμα. Η παρουσία του άγλυκου του λιγκστροσίδη στο εκχύλισμα μείωσε τη συγκέντρωση της ελαιοκανθάλης που απαιτείται για την κυτταροτοξικότητα.
Το άγλυκο του λιγκστροσίδη εμφανίζει πολλαπλασιαστική δράση έναντι ηπατοκυτταρικού καρκίνου σε ανθρώπινες κυτταρικές σειρές.
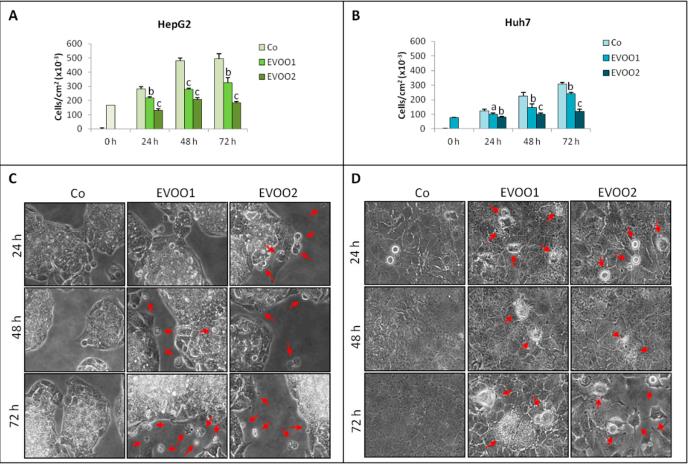
Fig. Phenolic extract reduces liver cancer cell proliferation. (A, C) Growth curve and morphological analysis on HepG2 cell line. (B, D) Growth curve and morphological analysis on Huh7 cell line. The cells were incubated for 24–72 h with two different doses of the extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO) extract.
