ΤΥΡΟΣΟΛΗ
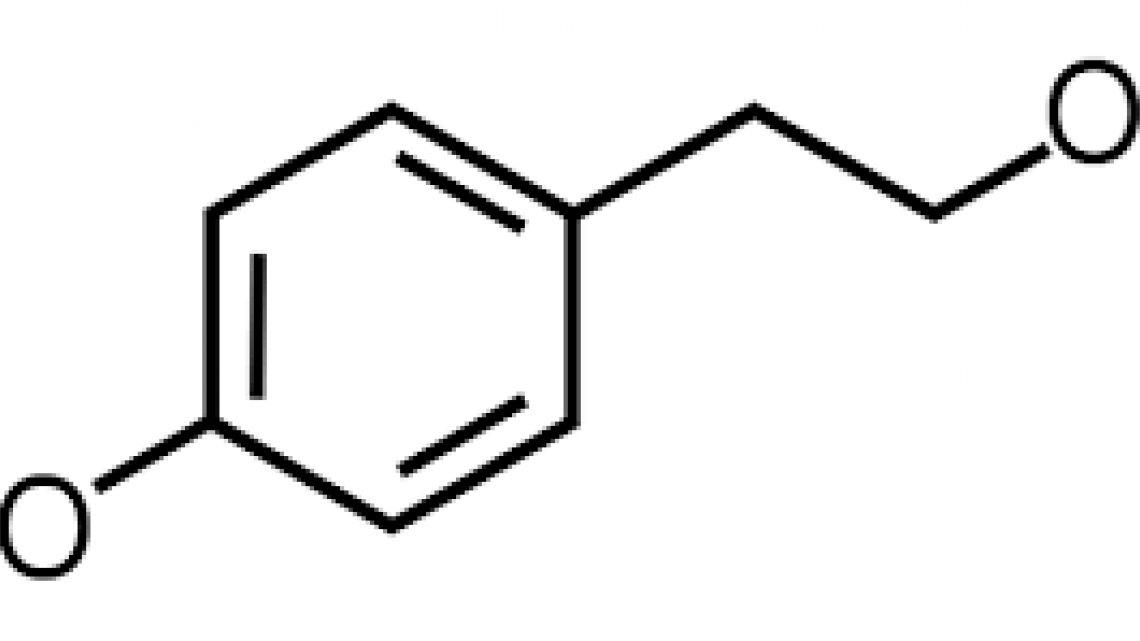
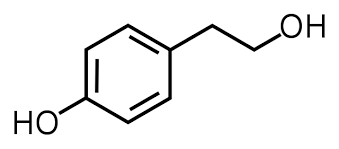
Η τυροσόλη είναι φυσική φαινολική ουσία που απαντάται κυρίως σε φυτά όπως π.χ. ελιές, αμπέλι και πεύκα. Χαρακτηρίζεται ως οργανική ένωση με τον χημικό τύπο HOC6H4CH2CH2OH που ταξινομείται ως φαινυλαιθανοειδές, ενώ αποτελεί και παράγωγο της φαιναιθυλικής αλκοόλης και απαντάται σε ποικιλία φυσικών προϊόντων. Ως ένωση, είναι άχρωμη, στερεή και δεικνύει χημική συμπεριφορά αλκοόλης. Ανευρίσκεται στα βασικά συστατικά -ωφέλιμα για την ανθρώπινη διατροφή- του ελαιόλαδου.[1][2]
Ως αντιοξειδωτική ουσία, η τυροσόλη μπορεί να προστατεύει τα κύτταρα από τραυματισμό λόγω οξείδωσης in vitro.[3] Αν και δεν είναι τόσο δραστική όσο άλλα αντιοξειδωτικά που υπάρχουν στο ελαιόλαδο (π.χ. υδροξυτυροσόλη), υψηλότερη συγκέντρωση και καλή βιοδιαθεσιμότητά της δείχνουν ότι δύναται να επιφέρει συνολική ωφελιμιστική επίδραση.[4]
Ως δραστική ουσία, μπορεί επίσης να είναι καρδιοπροστατευτική, αφού ζώα που υποβλήθηκαν σε θεραπεία με Trosol εμφάνισαν σημαντική αύξηση στη φωσφορυλίωση των Akt, eNOS και FOXO3a.[5] Επιπλέον, η τυροσόλη προκάλεσε επίσης την έκφραση της πρωτεΐνης SIRT1 στην καρδιά μετά από έμφραγμα του μυοκαρδίου σε ένα μοντέλο MI επίμυος. [6]
Παραπομπές
1.Charoenprasert, Suthawan; Mitchell, Alyson (2012). «Factors Influencing Phenolic Compounds in Table Olives (Olea europaea)». Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 60 (29): 7081–7095. doi:10.1021/jf3017699. PMID 22720792.
2.Karković Marković, Ana; Torić, Jelena; Barbarić, Monika; Jakobušić Brala, Cvijeta (2019). «Hydroxytyrosol, Tyrosol and Derivatives and Their Potential Effects on Human Health». Molecules 24 (10): 2001. doi:10.3390/molecules24102001. PMID 31137753.
3.«Tyrosol, the major olive oil biophenol, protects against oxidized-LDL-induced injury in Caco-2 cells». J. Nutr. 129 (7): 1269–1277. 1999. doi:10.1093/jn/129.7.1269. PMID 10395586.
4.«Tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol are absorbed from moderate and sustained doses of virgin olive oil in humans». European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 57 (1): 186–190. 2003. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601532. PMID 12548315.
5.«Akt/FOXO3a/SIRT1-Mediated Cardioprotection by n-Tyrosol against Ischemic Stress in Rat in Vivo Model of Myocardial Infarction: Switching Gears toward Survival and Longevity.». Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 56 (20): 9692–8. 2008. doi:10.1021/jf802050h. PMID 18826227.
6.Samuel, Samson Mathews; Thirunavukkarasu, Mahesh; Penumathsa, Suresh Varma; Paul, Debayon; Maulik, Nilanjana (2008-10-22). «Akt/FOXO3a/SIRT1-mediated cardioprotection by n-tyrosol against ischemic stress in rat in vivo model of myocardial infarction: switching gears toward survival and longevity». Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 56 (20): 9692–9698. doi:10.1021/jf802050h. ISSN 1520-5118. PMID 18826227.
